Marine Animals Definition Biology

Spicules- skeletal elements that support a sponge.
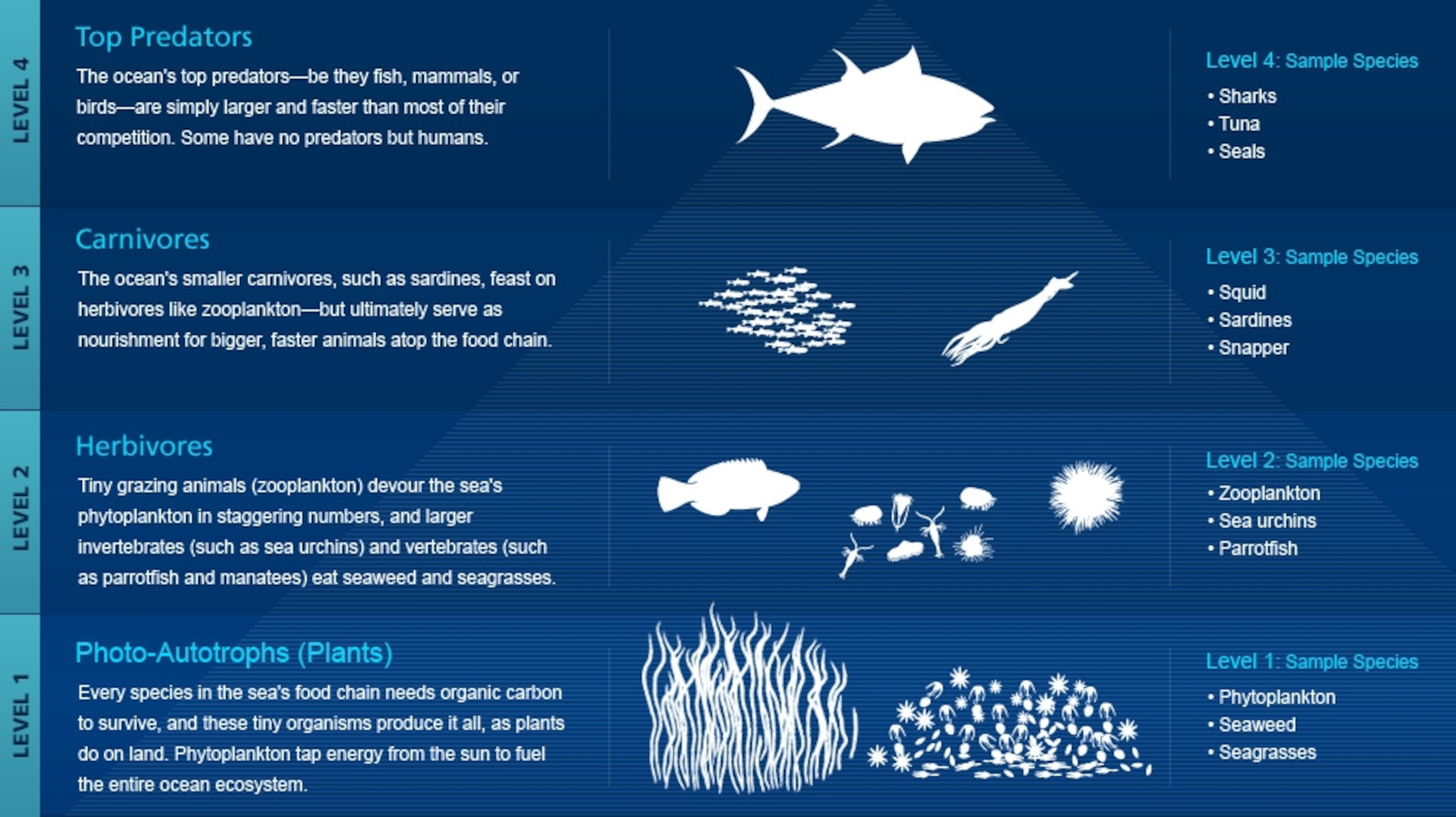
Marine animals definition biology. Marine biology is the study of plants and animals that live in saltwater therefore a marine biologist is someone employed in that field of study. But marine biology is so much more than making a dolphin -- or sea lion -- follow commands. So a marine biologist studies.
Marine biology is the study of animals that live in the oceans or other marine water bodies. An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs. There are a vast array of career choices one can pick from - from studying large ocean animals and what they eat to.
Our ocean coasts and estuaries are home to diverse living things. The study of marine life is called marine biology and a person that studies marine life is called a marine biologist. Osculum- large opening that lets water out.
Marine biology is the study of marine ecosystems marine organisms and human interactions with these environments and species. Marine biologist definition is - a scientist who studies life in the sea. Earth is often referred to as the blue planet because seas and oceans cover more than 75 of the Earths surface.
Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge. The scientific study of organisms living in or dependent on the oceans. Marine biologists may have many different jobs including working with marine mammals eg a dolphin researcher studying the seafloor researching algae or even working with marine microbes in a lab.
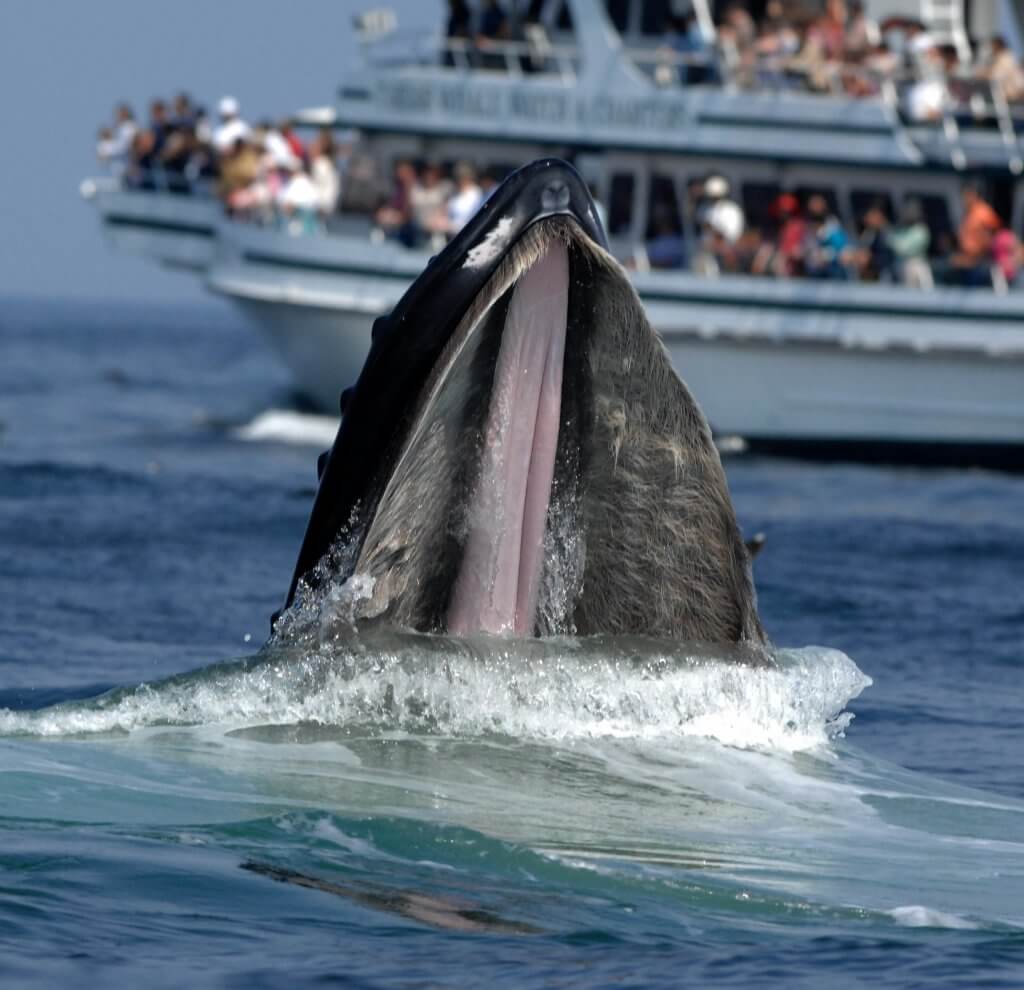
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life organisms in the sea. Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth. Marine biologists study biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical physical and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms.