Food Chain Definition Biology

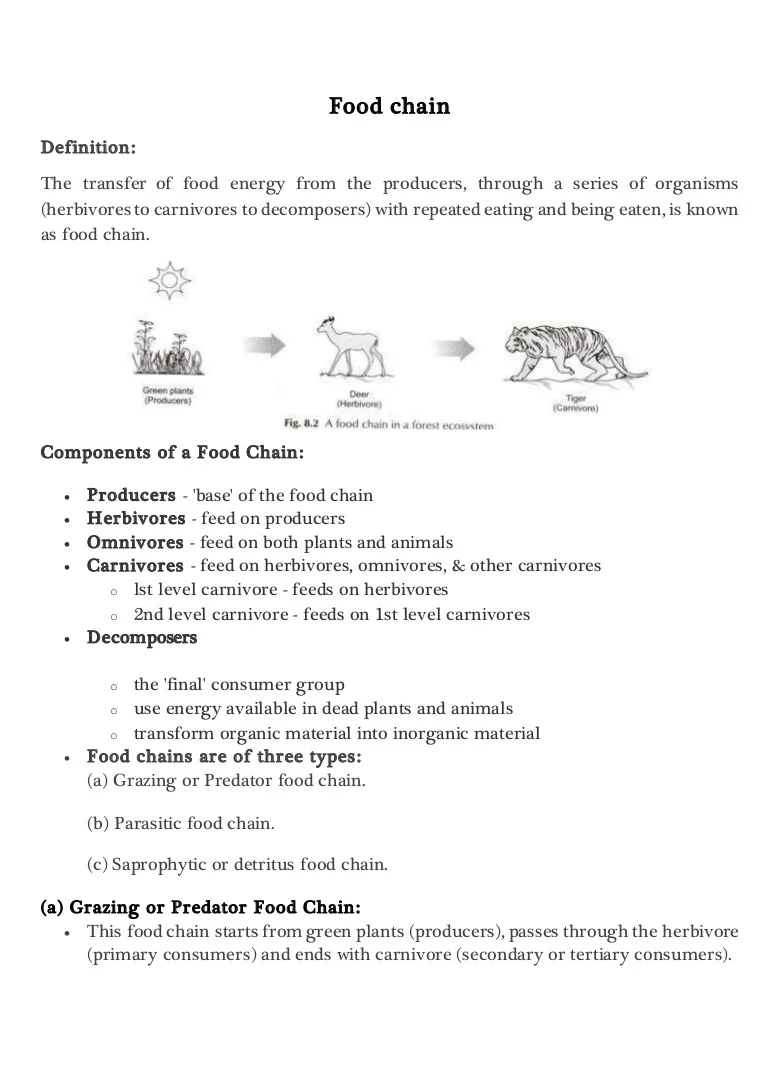
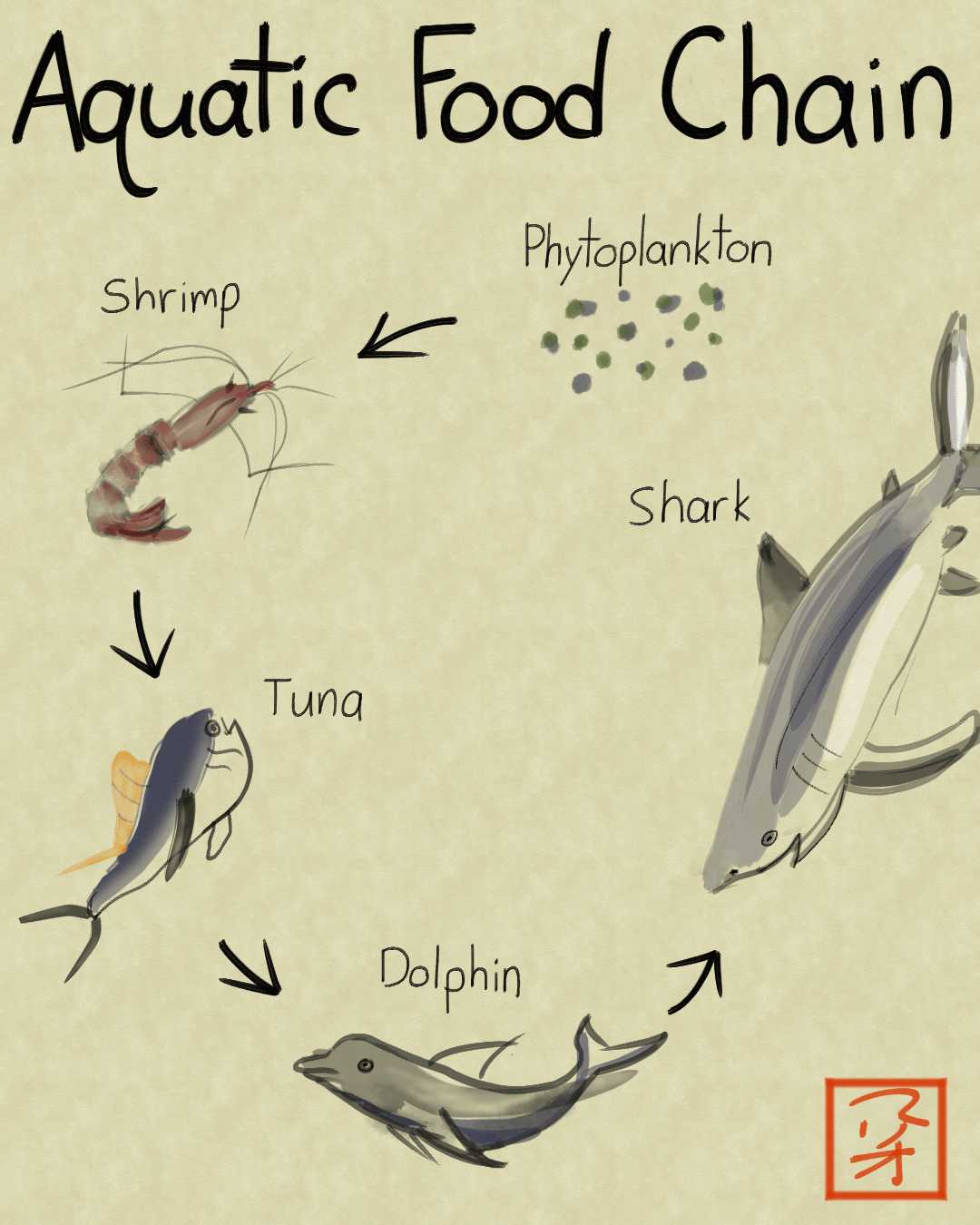
Food chain definition a series of organisms interrelated in their feeding habits the smallest being fed upon by a larger one which in turn feeds a still larger one etc.
Food chain definition biology. Environmental Studies ADVERTISEMENT. A is a diagram which depicts the series of organisms which eat each other. In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other.
Its name comes from the Greek trophies to feed to nourish. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. The organisms that feed on dead organic matter or detritus are known as detritivores or decomposers.
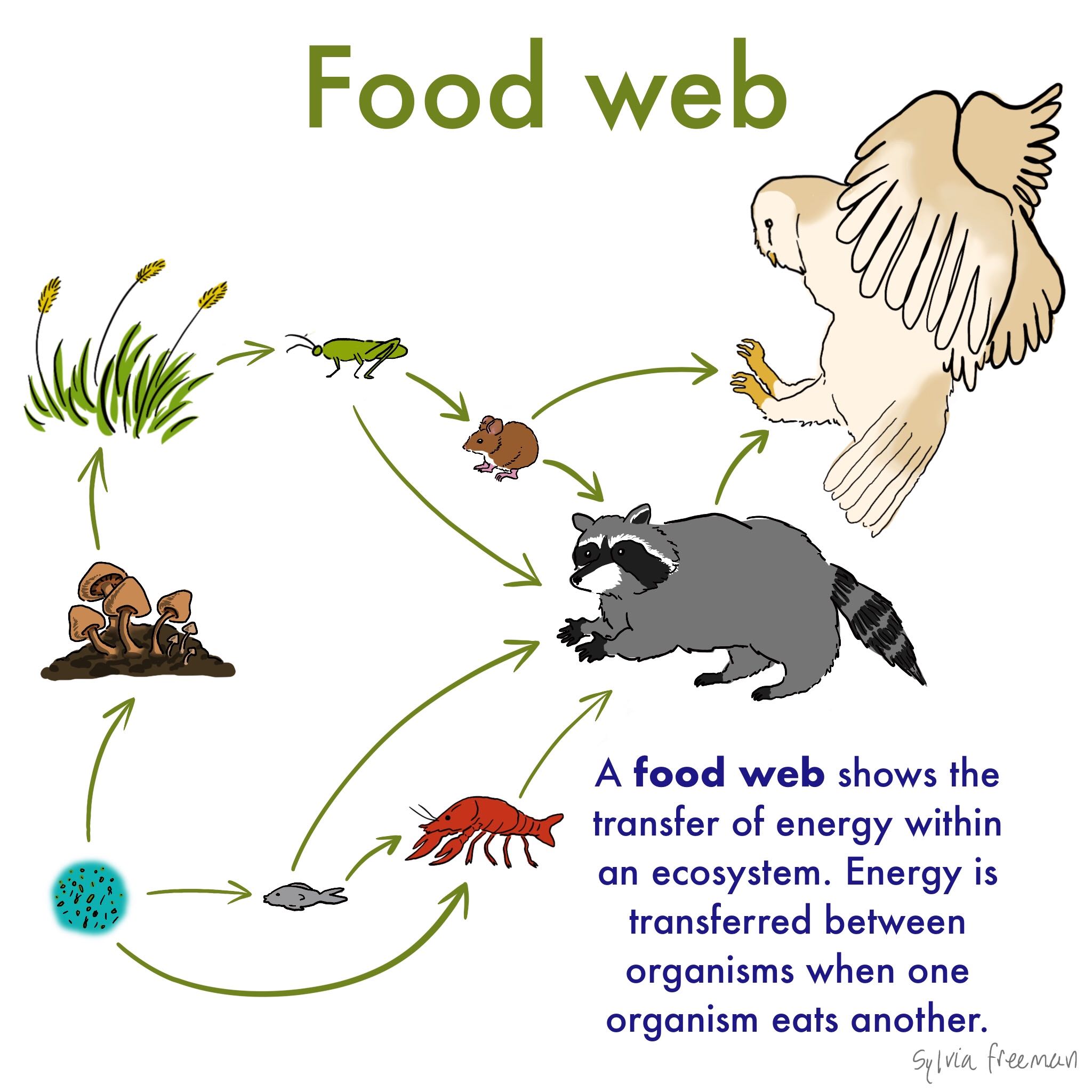
A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. The food chain can be defined as. That is they can form one of the links in a food chain.
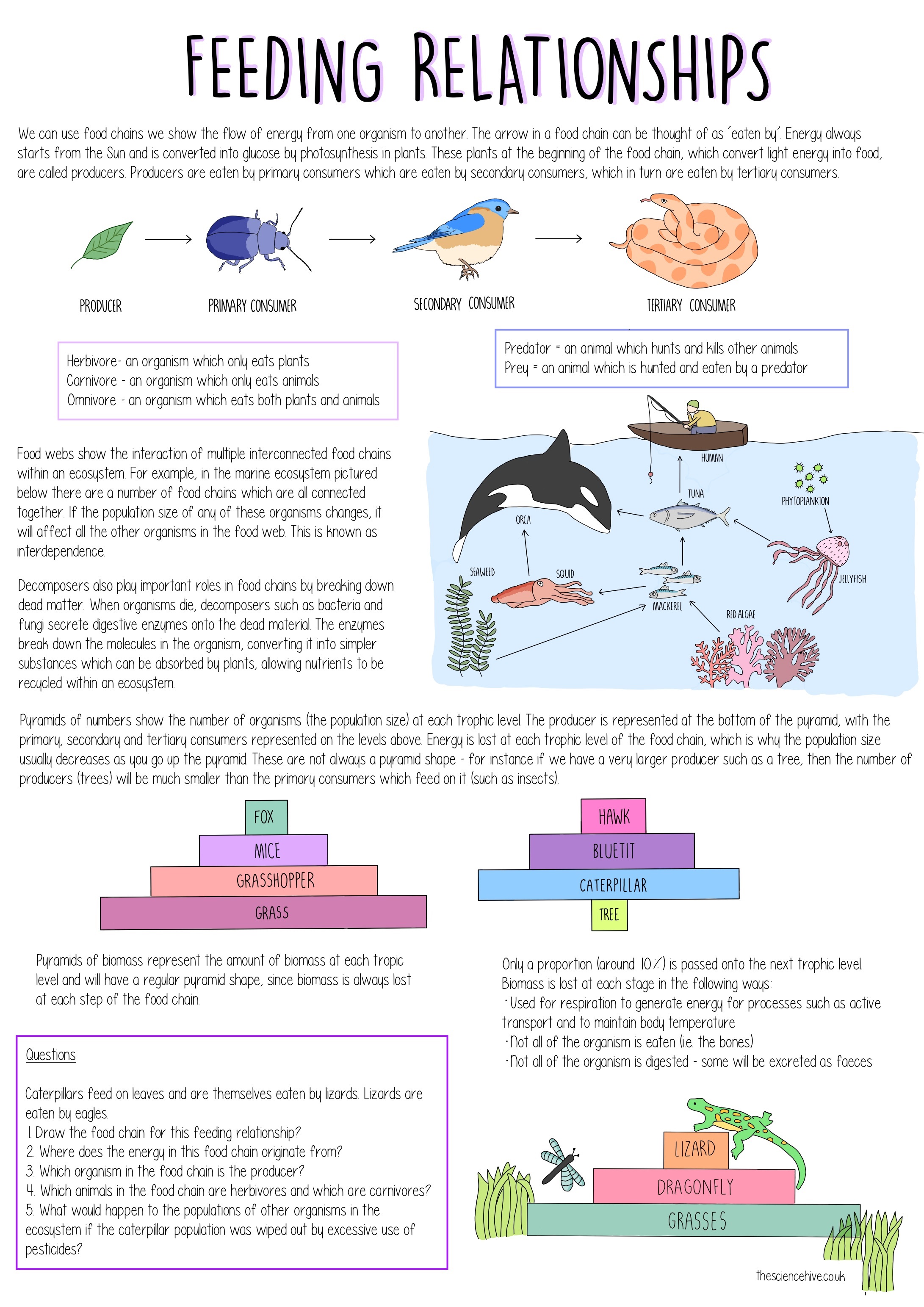
The arrows used to link each organism to the next represent the direction of energy flow. The feeding level is known as the trophic level. Definition of food webs- Food chains are not strictly linear they have branches type link one food chain with another there may be several interlinked food chains in a community and one animal may be a link in more than one food chains the process of interlink a network of food chain in a community is called food webs food webs includes all the feeding relationships in ecosystem.
A food chain is the linear not branched sequence in which a living organism serves as food for another starting with the producers and going up to the decomposers. These detritivores are later eaten by. A sequence usually shown as a diagram of feeding relationships between organisms showing who eats what and the movement of energy through trophic levels.
Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. For example if you had a hamburger for lunch you might be part of a food chain. Energy is not created or destroyed.