Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology
The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. Cellular respiration Energy from nutrients is converted into ATP. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP.
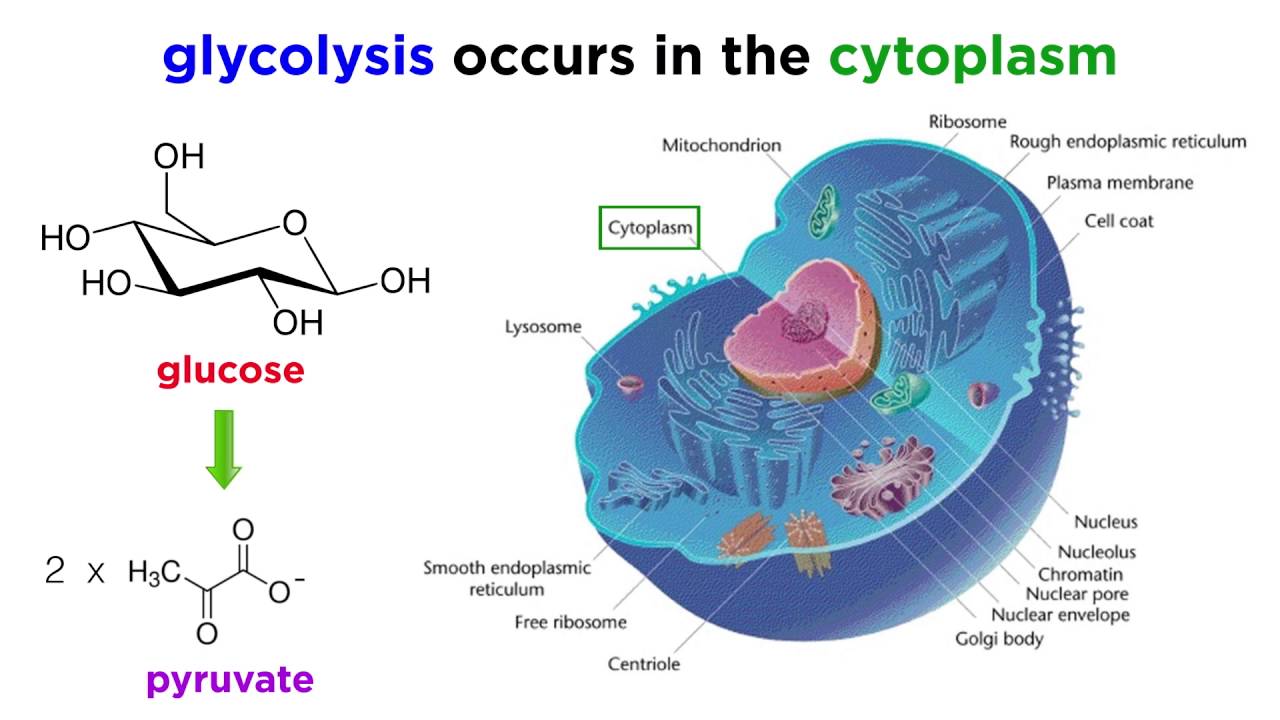
Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy.
Glucose and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecule eg. Related Biology Terms. A series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance eg.
Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. The cellular context In the diagram at left 1 represents the cell exterior. Hydrolysis Breaking a bond in a molecule and splitting it into smaller molecules through a reaction with water.
Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Cellular respiration biology definition. Where cellular respiration happens.
Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.



















